Many companies treasure knowledge and information as their top assets, but these assets are also prone to risks. With digital data exchanges becoming common, the security of valuable information is at risk like never before. As part of ISO 27001, an Information Security Management System (ISMS) offers a reliable way to manage risks and ensure protection.
In this article, we'll delve into what an ISMS is, its link to ISO 27001, why organisations need to adopt ISMS, and how you can implement one successfully.
In this blog post, we'll cover:
- How are ISO 27001 and ISMS related?
- Why is an Information Security Management System important?
- Who needs an ISMS and why?
- How does an ISMS work?
- How to implement an Information Security Management System (ISMS)
- What makes an ISMS implementation successful?
- What are the benefits of implementing an ISMS?
- Why do Information Security Management Systems need maintenance?
- Are there other standards that an ISMS must comply with besides ISO 27001?
- IT security vs cybersecurity vs information security: What’s the difference?
- Is implementing an ISMS different depending on the industry?
- FAQs
What is an Information Security Management System (ISMS)?
An information security management system (ISMS) is a set of policies and procedures that an organisation puts in place to protect its information assets. It explains and illustrates your organisation's approach to information security and privacy. It assists you in identifying and addressing the dangers and opportunities surrounding your important information and any linked assets.
That, in turn, protects your organisation from security breaches and minimises the impact of any disruptions that may occur. With the help of an Information Security Management System, you may comply with various regulations, including the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and ISO 27001 certification. The latter mainly focuses on the protection of 5 key components of information security.
What are the 5 components of information security management?
- Confidentiality - No one outside of the intended recipients can access or use the data in any way that is not explicitly authorised.
- Integrity - The data is free of errors and tampering, as well as being kept in a secure location.
- Availability - It becomes easier for authorised individuals to access and use this information.
- Authenticity - The identity of the authorised individual is confirmed to prevent unauthorised access.
- Non-repudiation - There is a clear record of the sender, receiver, delivery and receipt of the message so that neither party can deny the sending and receiving of data.
How are ISO 27001 and ISMS related?
ISO 27001 is an international standard for managing information security, which helps protect information assets and show your stakeholders you care about protecting their information. It’s why ISMS exists, as the essence of ISO 27001 is developing and maintaining an ISMS.
With cyberattacks seeing rampant growth, the ISO/IEC 27000 family of standards helps protect companies from potential online threats, and ISO 27001 is the world's best-known standard for information security management systems and their requirements.
The standard provides a set of controls for information security that an organisation needs to implement based on the results of a risk assessment and the requirements of interested parties. In other words, a combination of different types of controls will be implemented for each risk that needs to be treated.
You might also be interested: An essential guide to ISO 27001
Why is an Information Security Management System important?
The increased pressure on organisations to develop higher information security standards has raised interest in ISMS. Companies with complex supply networks are under the most strain - consider the SMEs in the automotive industry.
The same is true in regulated businesses such as banking, especially FinTechs and insurance companies, notably InsurTechs. Additionally, information security rules in healthcare are stringent. These industries have a regulatory emphasis that extends to company compliance.
Beyond industry-specific causes and needs, however, there is also a general trend toward greater information security. The following are a few reasons why organisations are under scrutiny when it comes to information security:
Cybercrime threatens your business
Cybersecurity is expanding because most firms can't afford data breaches. IBM's Security Cost of a Data Breach Report1 estimates that the average cost of a data breach in 2022 was $4.24 million—an amount that may put many companies out of business. According to a recent study, the cost of cybercrime worldwide is estimated to rise from $6 trillion to $10.5 trillion by 20252. This threatens your organisation’s future if you don't have the best information security experts protecting it.
Your processes are increasingly automated
More and more of your company's infrastructure is based on digital technology as various processes become increasingly automated. Every automated system is made up of code that can be accessed by criminals who hack into the system. Consequently, the more activities are done digitally, the more chances hackers have to obtain confidential information.
The number of vulnerabilities is growing
There is a wide range of technologies that may be exploited by hackers, not simply computers, websites, and servers. More items and systems than ever before are vulnerable to cyberattacks, from airline systems and automobile alarms to power grids and security systems.
Who needs an ISMS and why?
An ISMS is beneficial for any company, regardless of the industry or size. The majority, though, tend to be software-driven, digitised and SaaS-based companies. Health markets, for example, have strict minimum standards that must be observed in the field of information security to ensure medical confidentiality.
If we take the automotive industry, it focuses heavily on its products, which are intricate and involve numerous contributors. To ensure safety, there are strict approval procedures before vehicles can hit the road. Every party in the supply chain must adhere to industry-specific information security standards without any leniency.
How does an ISMS work?
Information security management systems in firms are process-oriented and always the responsibility of management. It is a top-down approach. Implementation, but not responsibility, can be delegated. Depending on the motive (see Figure below), management selects the procedures and methods to apply or build to ensure information security in corporate activities. The management must regularly examine the measures' scope, intensity, and progress.
The goal of an ISMS is not to achieve maximum information security. Rather, it is to attain the organisation's desired level of information security. Risk appetite is key. A corporation must know its information, risks, and the financial impact of a materialised risk. Based on this knowledge, the management must decide to what extent an ISMS should reduce the risks.
.jpg?width=1362&name=ISMS_EN%20(1).jpg)
What do you need to implement your ISMS?
Before starting to implement your ISMS, there are a few things you need to plan and consider:
1. Designated team
An ISMS that is ISO 27001 compliant or certified might be a difficult undertaking. To properly deploy an ISMS, you'll need a manager or team with the necessary time, resources, and expertise. Once your ISMS is up and running, your company will require the appropriate governance mechanisms to oversee it.
2. Resource overview
Many resources are utilised as part of a comprehensive ISMS. In addition to data, your company's software and hardware, physical infrastructure, and even its employees and suppliers can all be included. You'll need to do several things to keep track of them all in your ISMS. Using a systematic approach to risk management ensures the success of your entire organisation.
3. Actionable policies and restrictions in case of data breach
In the event of a data breach, your information security management system instructs your employees, suppliers, and other key stakeholders on how to keep their data safe. It is imperative that these information security practices and processes are established in clear, widely understood, and easy-to-implement policies and controls, as well. In this way, the advantages of your ISMS will be publicly known, and its integrity will be ensured.
4. Communication and engagement strategies for employees
Information security management systems must be the lifeblood of your organisation, according to ISO 27001 standards. Those who are interested in information security should be made aware of your ISMS, as well as the reasons for its importance and their duties in maintaining it. Nothing will be safeguarded if an ISMS is let to collect dust. It's critical to have the right tools and processes in place to get the job done. You may even have to conduct some information security education sessions.
5. Supply chain management tools and systems
Your information security management system will be used beyond the walls of your company. Your suppliers and other third parties may have access to or be responsible for crucial information on your behalf. ISO 27001 compliance may necessitate the compliance of your ISMS as well. It's important to ensure the integrity of your organisation by protecting yourself from any potential information security risks or challenges that your data may pose.
6. Working with third-party auditors and obtaining certifications
To get a comprehensive ISO 27001 certification, you will be audited by a third-party certification body (CB). A two-part certification process is in store for you. You’ll need to recertify every three years, and you’ll need to conduct frequent internal audits of your ISMS to meet the criteria.
7. Continual ISMS improvement and operating resources
Always on and aware, a good information security management system ensures the safety of sensitive information. As the organisation grows and develops, so does its information security infrastructure, which adapts to keep up with the ever-changing threats. Even if the system makes a mistake, it may use the information it gathers to keep improving–risk assessment and response are never finished.
Now that you know the resources you need to establish your ISMS, let us look at the steps to implement it.
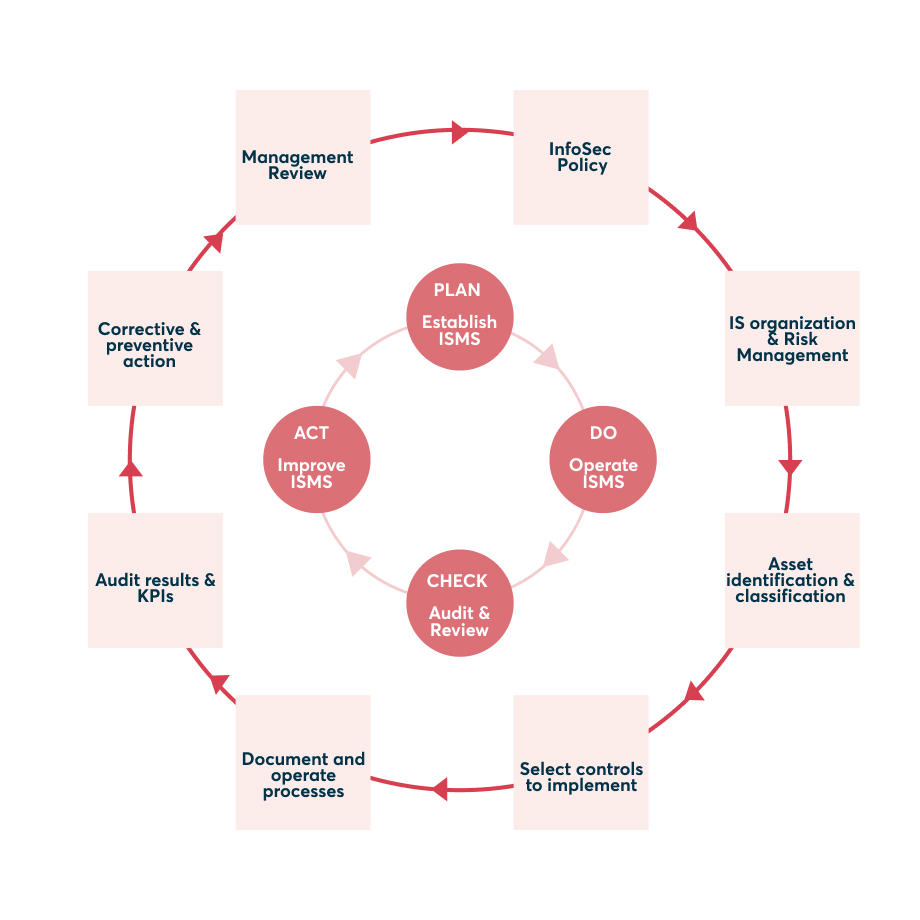
How to implement an Information Security Management System (ISMS)
The implementation and operation of an ISMS follow a classic PDCA cycle. PDCA stands for PLAN, DO, CHECK, ACT (see Figure below). The steps to take in detail are:
1. Create an ISMS policy
Why do you want to implement an ISMS? What goals do you expect to achieve with it? How will you implement such a system organisationally? Who assumes the role of the information security officer (ISO)? What resources does he/she have? What measures need to be taken?
2. Identify and classify assets
Which assets/information do you want to protect? How sensitive are these assets? For example, in the automotive industry, safeguarding images of a prototype vehicle, which hasn't been produced yet, is more critical than protecting images of a test model undergoing road tests just before its market release.
3. Establish ISMS organisation and risk management structures
Which tools do you want to use? What financial and human resources does the ISO have? Which structures should this establish?
4. Develop control mechanisms
How will you check whether the ISMS is effective and protects your company assets as desired?
5. Operate your ISMS
Which processes will you put into action in everyday life? How will you integrate and document them?
6. Check results and KPIs
Check this routinely: What results has your ISMS achieved? Which key performance indicators (KPI) can you measure?
7. Make corrections and take precautions
In which areas do you need to improve based on the results? How can you counter risks preventively?
8. Review by the management
Do the ISMS goals and the general orientation still fit, or are course corrections by the management needed? This should be analysed at least once a year.
What makes an ISMS implementation successful?
An ISMS can only be successfully implemented if it is truly desired by the company management and afforded the necessary resources. The 3 key factors that would determine the success of an ISMS are:
Management commitment
Management commitment plays an important role in ensuring that the ISMS implementer has a clear direction in implementing ISMS. Management activities include ensuring that the proper resources are available to work, training all employees affected by the ISMS structuring, hosting awareness programs and monitoring ISMS competency.
Implementer commitment
ISMS implementers need to have proper planning in their daily work schedule to ensure that appropriate time should be allocated to focus on ISMS processes in ensuring the success of ISMS implementation.
Implementer competency
Implementers must acquire at least three competencies to obtain appropriate skills and knowledge to comprehend the complete cycle of ISMS implementation. These skills include implementation and change management, awareness of standards, and the presentation of a method or framework for implementing, maintaining, monitoring, and improving information security.
What are the benefits of implementing an ISMS?
Nowadays, ISO 27001 plays a critical role in overall business growth. Having an ISO 27001-compliant ISMS means that:
1. You gain new business opportunities
Information security is a top priority for many organisations, so it’s not a surprise that suppliers insist that third parties follow best practices. Additionally, an ISMS pays off immediately when looking for potential investors: if there isn't one, a due diligence check is only possible to a limited extent.
2. GDPR compliance becomes easier
ISO 27001 helps organisations maintain effective information security controls by requiring them to examine the activities they've conducted consistently. A gap analysis will follow an ISMS audit to determine their current level of compliance.
3. Legal and regulatory compliance is ensured
Through your ISMS’s ISO 27001 certification, you can ensure that your organisation complies with all national regulations, not only GDPR.
4. Develop a competitive edge
Your high information security standards can attract more customers and improve your competitive status. In any case, an ISMS increases the value of organisations because only an ISMS provides a precise overview of the processes and informational assets in your own company.
5. Increase resilience to attacks and errors
When a company has high levels of cyber resilience, it is better equipped to withstand cyberattacks, limit the damage they do, and continue operating in the event of an attack.
6. Manage your information in one system
An ISMS acts as a centralised hub for safeguarding and managing all of your company's information in one location.
7. Evolve to adapt to newer security threats
Keeping pace with both external and internal changes, an ISMS minimises the possibility of ever-changing risks.
8. Improve company culture
Rather than focusing just on IT, an ISMS takes a comprehensive approach to security. This makes it easier for staff to grasp the dangers and incorporate security measures into their daily routines.
9. Lower costs related to InfoSec
Using an ISMS-based risk assessment and analysis strategy, organisations may save money by not overspending on defence technologies that do not apply to them.
Why do Information Security Management Systems need maintenance?
Your ISMS will likely have a few flaws, and its controls won’t work perfectly after the initial setup. An ISMS needs continuous maintenance and updating to run successfully like any other process.
Constant improvement and maintenance keep your ISMS’s policies and procedures up to date, which will continue to support protecting your sensitive information.
Are there other standards that an ISMS must comply with besides ISO 27001?
ISO 27001 could be described as the gold standard for Information Security Management Systems. Other standards, such as the ones mentioned below, may be considered depending on the industry, market and national legislation.
Cyber Essentials Scheme
The Cyber Essentials Scheme, introduced by the UK's National Cyber Security Centre, is an effective government-backed scheme that helps protect your organisation against a range of the most common cyberattacks.
The NIST Standard
The NIST Standard (National Institute of Standards and Technology) 800-53 is important for cooperation with US government information systems. Generally speaking, NIST guidance provides a set of standards for recommended security controls for information systems at federal agencies.
SOC 1 and SOC 2
The International Service Organisation Control Standards SOC 1 and SOC 2 can also be relevant to a company's financial reporting. SOC 1 reports focus on financial reporting controls, whereas SOC 2 reports focus on service organisations' operational and compliance controls.
CPPA
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) protects the privacy of California residents. Individual data, such as internet activity, cookies, IP addresses, and biometric data, will be regulated by the CCPA, as will "household data" collected by IoT devices in the home, for example. Consumers have the right under the CCPA to know what personal data is collected or sold and for what purpose, as well as disclosures of past transactions dating back to January 1, 2019. (the date on which the act was established).
HIPAA
The HIPAA Privacy Rule protects medical records and other personally identifiable information. It applies to health plans, clearinghouses, and providers who perform electronic transactions. The Rule puts restrictions and conditions on the uses and disclosures of protected health information without an individual's consent.
LGPD
LGPD, Brazil's General Data Protection Law, is the country's reaction to the EU's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). In principle, the LGPD mandates that you only process personal data of Brazilian individuals for legitimate, precise, explicit, and declared objectives.
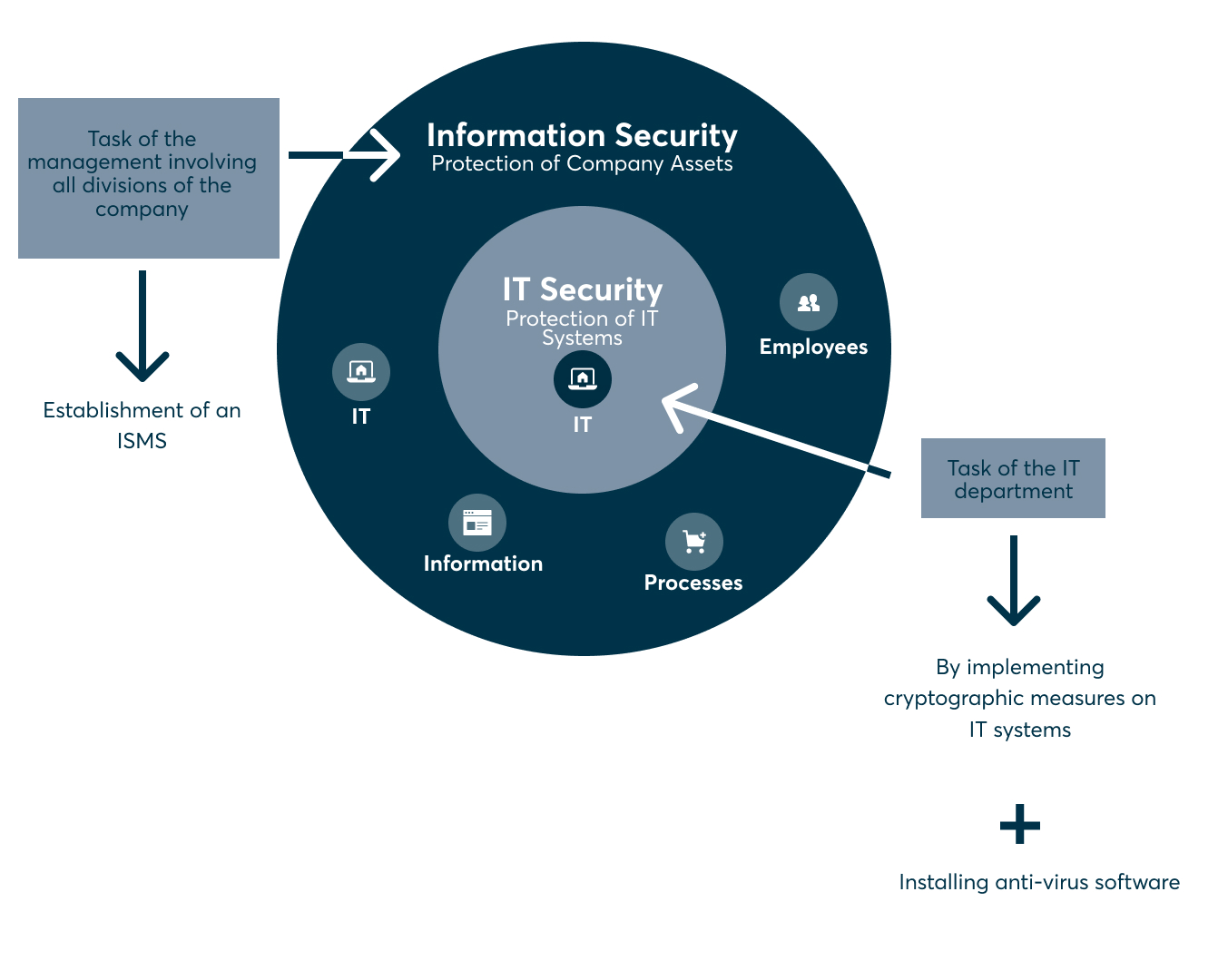
IT security vs cybersecurity vs information security: What’s the difference?
Business owners may sometimes be unaware of the differences between IT security, cybersecurity and information security, and it may lead them to believe that one can be substituted for the other.
This is not the case.
IT security refers to safeguarding all IT assets within an organization, while cybersecurity specifically focuses on defending against cyber threats targeting digital information and network-connected systems.
Information Security (Infosec), on the other hand, focuses on securing data wherever it is stored. Keeping information private, secure, and accessible is the primary goal. Consequently, the scope of Infosec is significantly larger than CyberSec since it covers safeguarding data and information held in both physical locations (such as desks and cabinets) and IT systems.
To further illustrate the differences between Infosec and CyberSec, here are a few examples:
- Value of data - The value of data is the most important component of both Infosec and CyberSec. The most important data in your company should be safeguarded to the fullest extent possible. Protecting your company's business information and IT systems is the goal of CyberSec, which aims to prevent digital hacking. Infosec aims to defend the value of your company's information assets from any sort of danger, digital or otherwise.
- Security professional priorities - Active threats, such as hacking attempts and viruses, are the main focus of CyberSec specialists. Infosec professionals have a wider scope, which includes policies and procedures, as well as organisational responsibility for ensuring security.
- Focus of Infosec vs Cybersec - Outside dangers to an organisation's digital infrastructure are the primary focus of Cybersec. The goal of Infosec is to safeguard the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of all forms of information assets through the implementation of policies and procedures.
- Threats - Where CyberSec is only concerned with cyber threats, Infosec is concerned with threats of all types, like human error.
Is implementing an ISMS different depending on the industry?
The relevant standard, ISO 27001, does not provide any information on this. It does not differentiate according to industry or company size but defines the general requirements and addresses 14 security-relevant areas. These are the same areas that are also inspected carefully during the due diligence check.
In a nutshell: The same framework conditions always apply, but the implementation of the processes and measures can be different depending on the industry and the size of the company.
Start building your ISMS
In terms of information security, an ISMS ensures transparency, as well as predictable processes and KPI results. In other words: With a well-implemented ISMS, there are no surprises when it comes to information security issues. Benjamin Franklin is credited with a phrase that inversely sums up the benefits of an ISMS: “When you fail to prepare, you prepare to fail.”
Looking for guidance in understanding ISMS or preparing for ISO 27001 certification? Our team of experts is ready to assist you. Feel free to reach out:
FAQs
What is information security and information security management?
Information security, sometimes shortened to InfoSec, is the practice of protecting information by mitigating information risks.
InfoSec management is the process of defining and managing the controls a business needs to put in place to protect its assets' privacy, availability and integrity from threats and weaknesses.
As part of information security management, a business may implement an information security management system and other best practices found in the ISO 27001 standard.
How can you improve information security in an organisation?
- Train your employees on InfoSec best practices
- Regularly check for software vulnerabilities
- Physically protect your network with secure hardware
- Implement or improve access control
- Use encryptions and firewalls.
Is providing data security training to employees part of ISMS policy?
If an organisation wants to adopt an ISMS that complies with ISO 27001, clause 7.2.2 requires it to give information security awareness training to its staff. To ensure the safety of your business, it is crucial to provide your staff with the resources and encouragement they need to do their jobs effectively.









