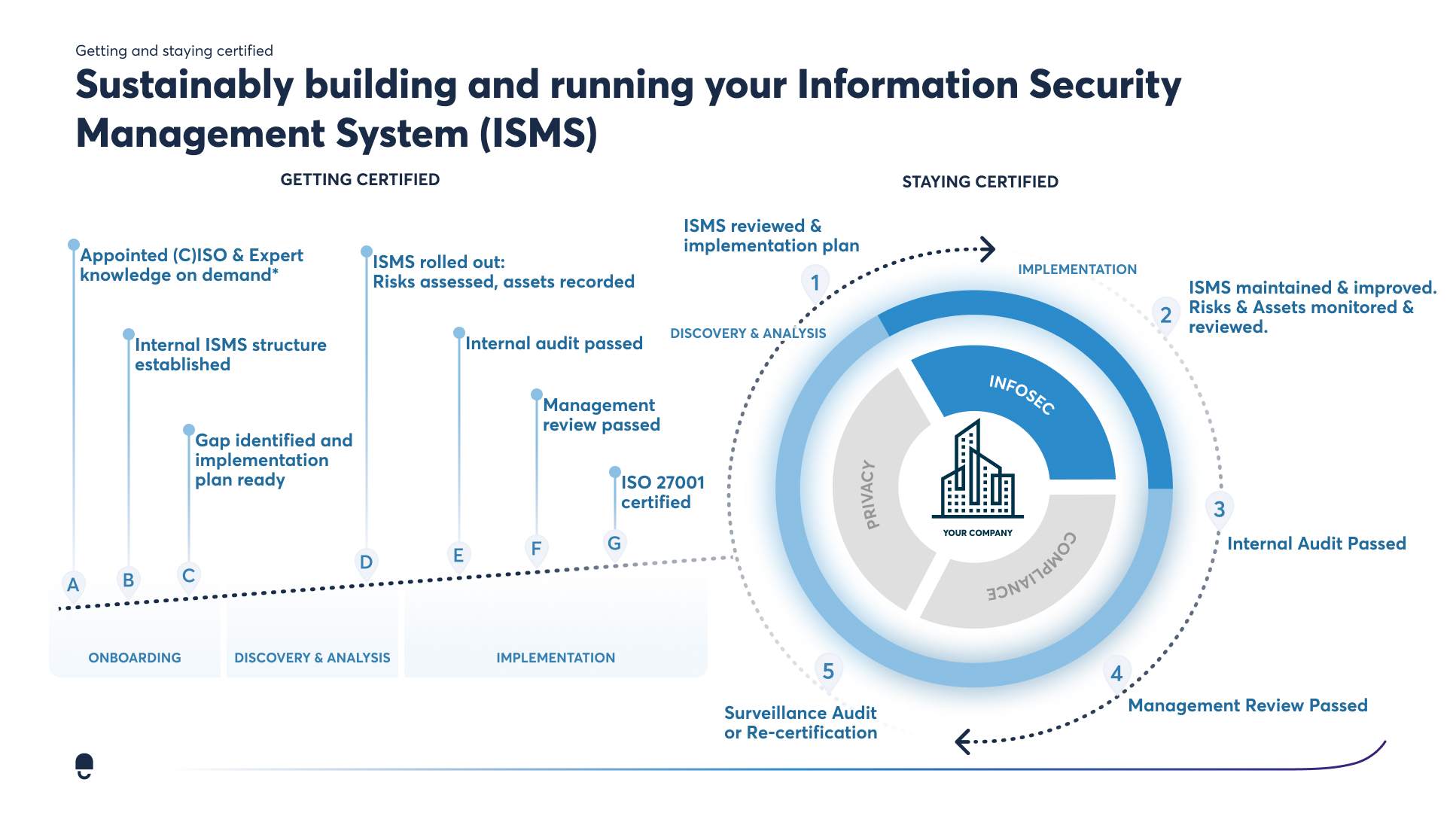
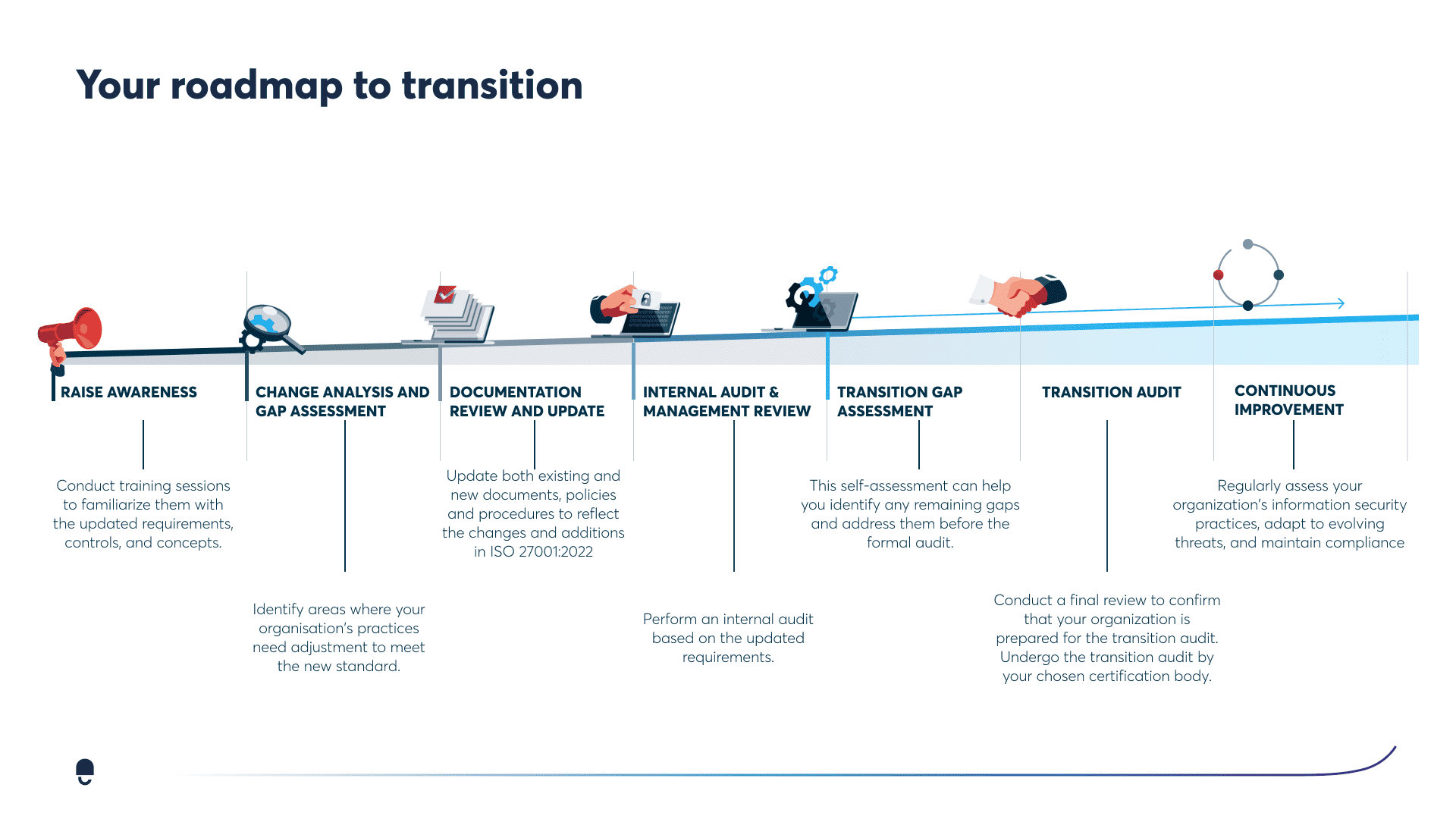
Complete your ISMS Documentation
Documentation is the basis of your ISMS and the most important part of getting and maintaining your certification. If it's not documented, it's not relevant.
You need to keep track of many things when it comes to documentation, as there are many things to consider. To give you a complete overview of the documentation required for ISO 27001 certification, along with information on preparing said documentation, we have created a detailed list for the documentation:
Definition of the scope of application of the ISMS (Information Security Management System)
The scope of application of the ISMS is defined in the so-called “Scope Document”. This determines which divisions of your company are subject to the ISMS. Your ISMS doesn’t necessarily need to be rolled out across the entire company - only the relevant departments and divisions. That said, in the case of smaller companies, it will usually cover all departments.
%20.webp?width=1600&height=400&name=Definition%20of%20the%20scope%20of%20application%20of%20the%20ISMS%20(Information%20Security%20Management%20System)%20.webp)
Coordination and documentation of the guideline on information security
The objectives which your company seeks to achieve with your ISMS should be clearly defined in the guideline on information security. This document should also demonstrate why information security is a top priority in your organisation, and that management is responsible for the guideline.
This does not have to be formulated by management themselves but must always be approved by the necessary stakeholders. The ISO standard already specifies the following information security objectives:
- Data confidentiality
- Data availability
- Data integrity
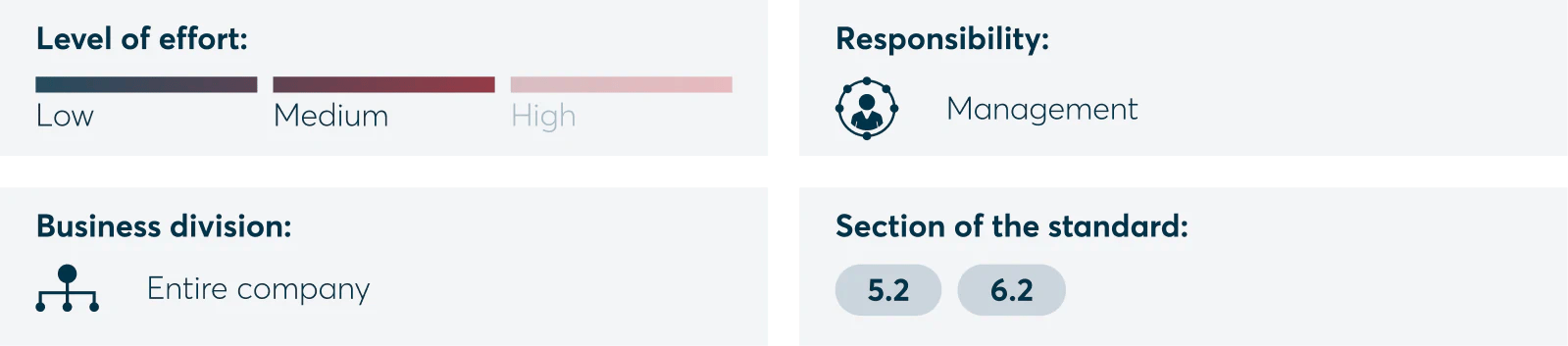
Definition of risk assessment and risk management methods
You will need to identify your company’s risks, assess them individually and define an appropriate methodology for risk management. The assessment should always be carried out by the respective risk owner and should ultimately be approved by management.
In addition, this area should be coordinated within the company, ideally with your ISO, CISO or risk management department. Given that this process must be repeated on a regular basis, it can result in a lot of effort, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises that lack in-house security and risk experts. Repetitions occur when there are new assets in the company that require a risk assessment.
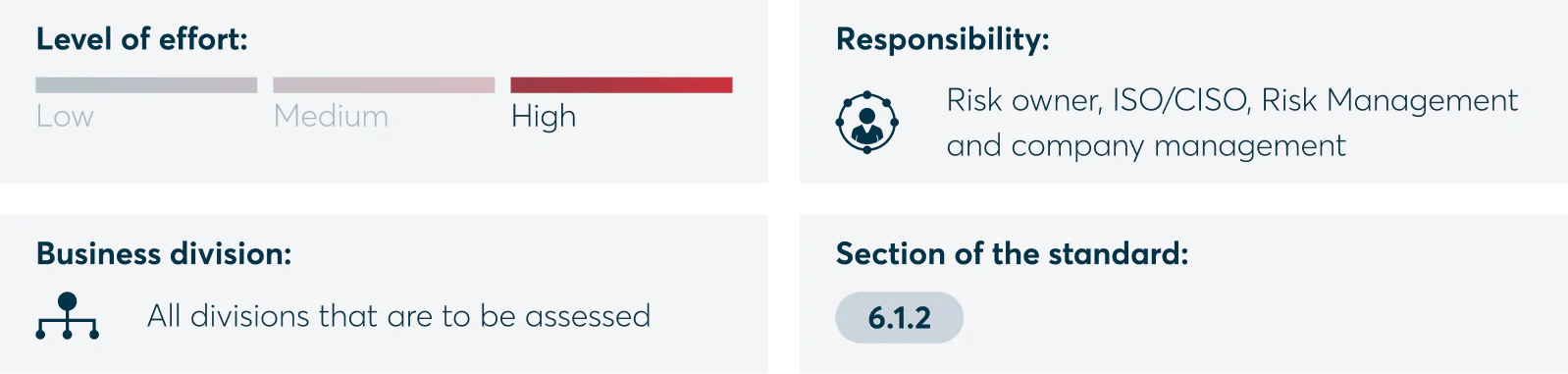
Preparing a declaration of applicability
As part of this step the ISO/CISO shall agree, with the respective specialist departments, which of the 93 controls stated in Appendix A of ISO 27001:2022 must be carried out or which are relevant for the company.
ISO 27001 has specified various areas such as cryptography, HR security or operational security. Companies may exclude some of these areas by providing appropriate justification. For example, if a business does not have a loading zone, it is simply not necessary to draw up rules for loading zones.
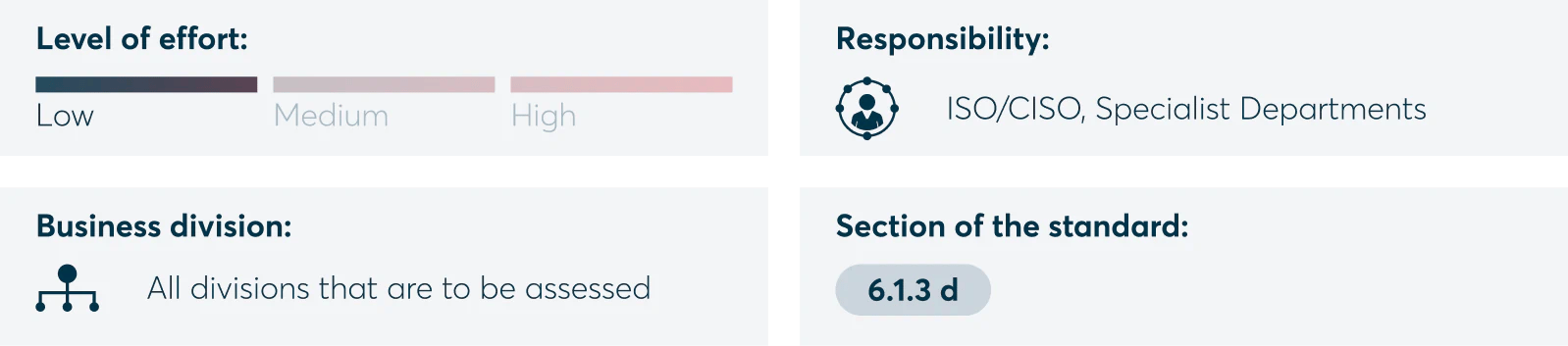
If you choose to work with experts such as DataGuard or an external consultant, you may receive documentation templates that will help cut down on your manual work significantly compared to creating them from scratch.


%20.webp?width=1600&height=400&name=Definition%20of%20the%20scope%20of%20application%20of%20the%20ISMS%20(Information%20Security%20Management%20System)%20.webp)



