Navigating the transition to ISO 27001:2022
The transition to ISO 27001:2022 is a significant undertaking, but it is one that can be made easier with the right knowledge and resources. This guide provides you with everything you need to know to navigate the transition process successfully.
We will begin by demystifying ISO 27001 and explaining why it is important for your organisation. We will then discuss the key changes in the new standard and how they can benefit your organisation. Finally, we will provide you with a roadmap for transitioning to ISO 27001:2022, as well as tips for maximising the benefits of the transition.
What to expect in this guide
A quick overview of ISO 27001:2022: We will briefly explain what ISO 27001 is and why it is important.
Importance of Transition: We will discuss why transitioning to ISO 27001:2022 is essential and what it can offer your organisation.
Transition Timeline: We will provide you with a clear overview of the transition deadlines and milestones so you can plan your journey accordingly.
Key Changes in ISO 27001:2022: We will explore the significant changes in this edition, focusing on risk, people, emerging threats, and flexibility.
Revamped Annex A Controls: We will explain the newly structured Annex A controls and how they can simplify compliance.
Your Transition Roadmap: We will provide you with a structured roadmap for transitioning to ISO 27001:2022, from awareness to continuous improvement.
Proactive Strategies: We will share tips on how to maximize the transition as an opportunity for overall improvement and enhanced communication.
ISO 27001:2022: The new standard for information security
ISO 27001 is the international standard for information security management systems (ISMS). It provides organisations with a framework for managing their information security risks and protecting sensitive data.
The latest version of ISO 27001, published in 2022, includes several significant changes. These changes are designed to make the standard more relevant to the current threat landscape and to help organisations improve their information security posture.
Why is it important to transition to ISO 27001:2022?
There are a number of reasons why it is important for organisations to transition to ISO 27001:2022. These include:
- To comply with the latest international standards for information security.
- To protect sensitive data from cyber threats.
- To demonstrate to customers, partners, and other stakeholders that the organisation is committed to information security.
- To improve the organisation's overall risk management processes.
- To reduce the risk of data breaches and other incidents.
- To improve the organisation's efficiency and effectiveness.
- To further improve the maturity of CIA (Confidentiality, Integrity and Availability of data).
Your ISO 27001 certification process made easy.
Get ISO 27001 certified in as little as 3 months.

ISO 27001:2022 transition timeline
The transition period for ISO 27001:2022 began on October 31, 2022, and will end on October 31, 2025.
During this time, organisations that are already certified to ISO 27001:2013 have three years to transition to the new standard.
Organisations that have not yet started their ISO 27001 certification journey have until April 1, 2024, to become certified to the new standard.
Here is a detailed timeline of the transition period:
- October 31, 2022: The transition period begins.
- May 1, 2024: All initial (new) certifications should be to the ISO 27001:2022 edition.
- July 31, 2025: All transition audits should be conducted by this date.
- October 31, 2025: The transition period ends. Certificates for ISO/IEC 27001:2013 will no longer be valid after this date.
Organisations that are already certified to ISO 27001:2013:
- Can continue to operate under their existing certification until October 31, 2025.
- Must transition to ISO 27001:2022 by this date (October 2025).
- Can choose to transition at any time during the transition period.
- May need to undergo a transition audit to verify their compliance with the new standard.
Organisations that are already certified will have until the 31st of October 2025 as the deadline to transition. As of that date, all certifications for ISO 27001:2013 will expire and will no longer be considered valid.
In the meantime, organisations should continue to manage and improve their existing 27001:2013 ISMS in conjunction with planning a transition audit. If your company is not certified yet but still wants to certify against the 2013 revision, you can do so up to the 31st of October, 2024.
But generally speaking, the sooner you comply with ISO 27001:2022 — the better. It will save you time, money and frustration.
Kyle Tackley
Team Lead – UK Tech and Privacy Practice
Organisations that have not yet started their ISO 27001 certification journey:
- Must become certified to ISO 27001:2022 by April 1, 2024.
- Can choose to become certified to ISO 27001:2013, but this will not give them any additional time to transition to the new standard.
- It is important to note that the transition period is not a grace period. Organisations that do not transition to ISO 27001:2022 by October 31, 2025, will no longer be compliant with the standard, and their certificates will be invalid.
Here are some additional things to keep in mind about the transition timeline:
- The transition period is designed to give organisations enough time to implement the changes required by ISO 27001:2022.
- However, organisations may need to start the transition process sooner if they have a significant amount of work to do.
- The transition process can be complex and challenging, so it is important to start planning early.
- There are a number of resources available to help organisations with the transition process, such as ISO's own guidance document.
Watch the “ISO 27001:2022 Your Practical Transition Guide” on-demand webinar here.
What are the key changes in ISO 27001:2022?

The new edition of ISO 27001 introduces several significant changes, including:
A focus on risk-based thinking
The new standard emphasizes the importance of organisations understanding their information security risks and taking steps to mitigate those risks. This is a major change from the previous version, which focused on a more prescriptive approach to information security.
A greater emphasis on the importance of people and culture
The new standard recognizes that people are a critical element of any information security program. It emphasizes the importance of creating a culture of information security within the organisation. This includes things like training employees on information security best practices and promoting a security-minded mindset throughout the organisation.
The introduction of new controls to address emerging threats
The new standard includes a number of new controls to address emerging threats, such as cloud computing, social engineering, and data breaches. These new controls are designed to help organisations stay ahead of the curve and protect their information assets from the latest threats.
A new way of breaking down the standard
The new standard changes the layout of the Annex A controls to be broken down into smaller groups. These controls now evolve around what they most protect and thus simplifying what was once a more complicated breakdown.
Get ISO 27001 certified real fast with experts at your side.
Reduce manual work by up to 75%.
100% first-try pass rate in external audits on ISO 27001

What has changed in ISO 27001:2022?
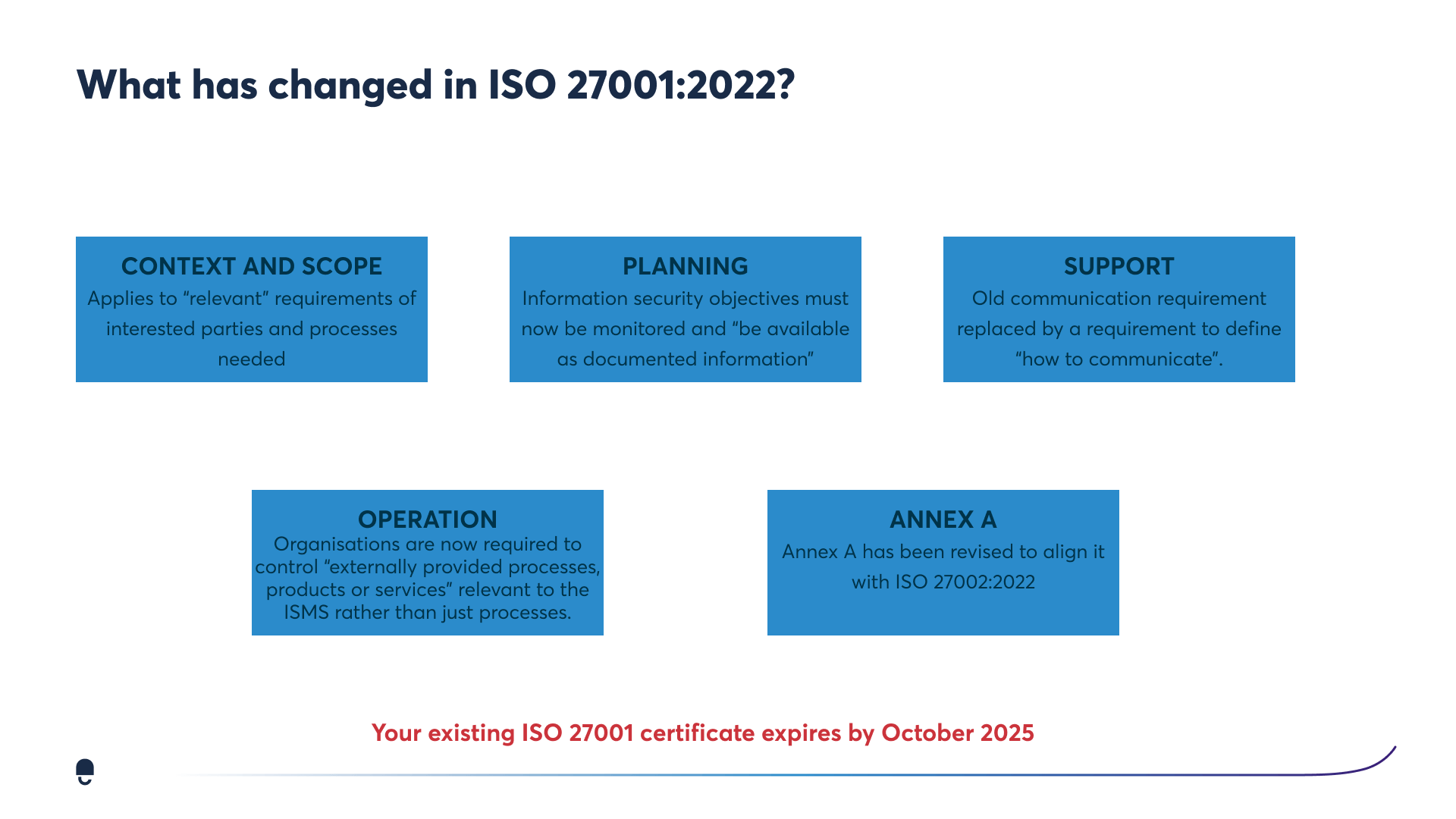
Here are some of the specific changes in each clause of the standard:
Context and Scope: The scope clause now applies to "relevant" requirements of interested parties and processes. This means that organisations need to consider the needs of all of their stakeholders, not just their customers and suppliers.
Planning: The planning clause now requires organisations to define their information security objectives and to monitor and review those objectives on a regular basis. This is a change from the previous version, which only required organisations to define their information security policies.
Support: The support clause now requires organisations to define how they will communicate information security risks and issues to their staff. This is a new requirement in the new standard.
Operation: The operation clause now requires organisations to control "externally provided processes, products, or services" that are relevant to their ISMS. This is a change from the previous version, which only required organisations to control their own processes and systems.

The new structure of Annex A controls in ISO 27001:2022
The new edition of ISO 27001 restructures the Annex A controls into four categories: organisational, people, physical, and technological. This is a significant improvement over the previous version, which had 14 control domains. The new structure is designed to make it easier for organisations to select and implement the controls that are most relevant to their needs.
- The organisational category contains 37 controls that address the overall management of information security within an organisation. These controls include things like establishing an information security policy, appointing a security manager, and conducting risk assessments.
- The people category contains 8 controls that address the role of people in information security. These controls include things like training employees on information security best practices, conducting background checks on new hires, and managing user access to sensitive information.
- The physical category contains 14 controls that address the physical security of information assets. These controls include things like securing buildings and facilities, protecting computer rooms, and managing the disposal of sensitive information.
- The technological category contains 34 controls that address the technological aspects of information security. These controls include things like implementing firewalls and antivirus software, encrypting data, and managing access to information systems.
The new structure of Annex A controls is aligned with the four pillars of information security:
- Organisational: This pillar addresses the need for a strong organisational commitment to information security.
- People: This pillar addresses the importance of people in information security.
- Physical: This pillar addresses the need to protect information assets from physical threats.
- Technological: This pillar addresses the need to protect information assets from technological threats.
The new structure of Annex A controls is a significant improvement over the previous version. It makes it easier for organisations to implement an effective information security management system and protect their information assets from a wide range of threats.
In addition to the new structure, ISO 27001:2022 also includes 11 new controls. These controls are designed to address emerging threats, such as cloud computing, social engineering, and data breaches. The new controls are also designed to improve the effectiveness of information security management systems by providing organisations with more options for mitigating risks.

The new controls are as follows:
Threat intelligence: This involves the collection and analysis of information about potential threats to information security within organisations.
Information security for the use of cloud services: Assessing and managing the risks associated with the use of cloud services.
ICT readiness for business continuity: Ensuring that information and communications technology (ICT) systems remain resilient and operational in disaster scenarios is a requirement.
Physical security monitoring: Continually monitoring the physical security systems to promptly identify and respond to security incidents.
Configuration management: Managing the configuration of their information systems to ensure that they are secure.
Information deletion: Securely deleting sensitive information when it is no longer needed.
Data masking: Masking sensitive information to prevent unauthorized access.
Data leakage prevention: Preventing sensitive information from being leaked outside of the organisation.
Monitoring activities: Monitoring the information security activities to ensure that they are effective.
Web filtering: Filtering web traffic to prevent access to malicious websites.
Secure coding: Developing and using secure code to protect the information systems.
Through these new Annex A controls, many organisations may be required to implement 20+ new ISMS documents, policies and procedures into their ISMS based on their scope and requirements.
DataGuard helped us get ISO 27001 certified 50% faster.
Reece Couchman
CEO & founder at The SaaSy People
100% first-try pass rate in external audits on ISO 27001
Your roadmap to transition to ISO 27001:2022
The transition to ISO 27001:2022 can be a daunting task, but it is important to remember that it is a journey, not a destination. By following a structured roadmap, you can make the transition smoother and more successful.
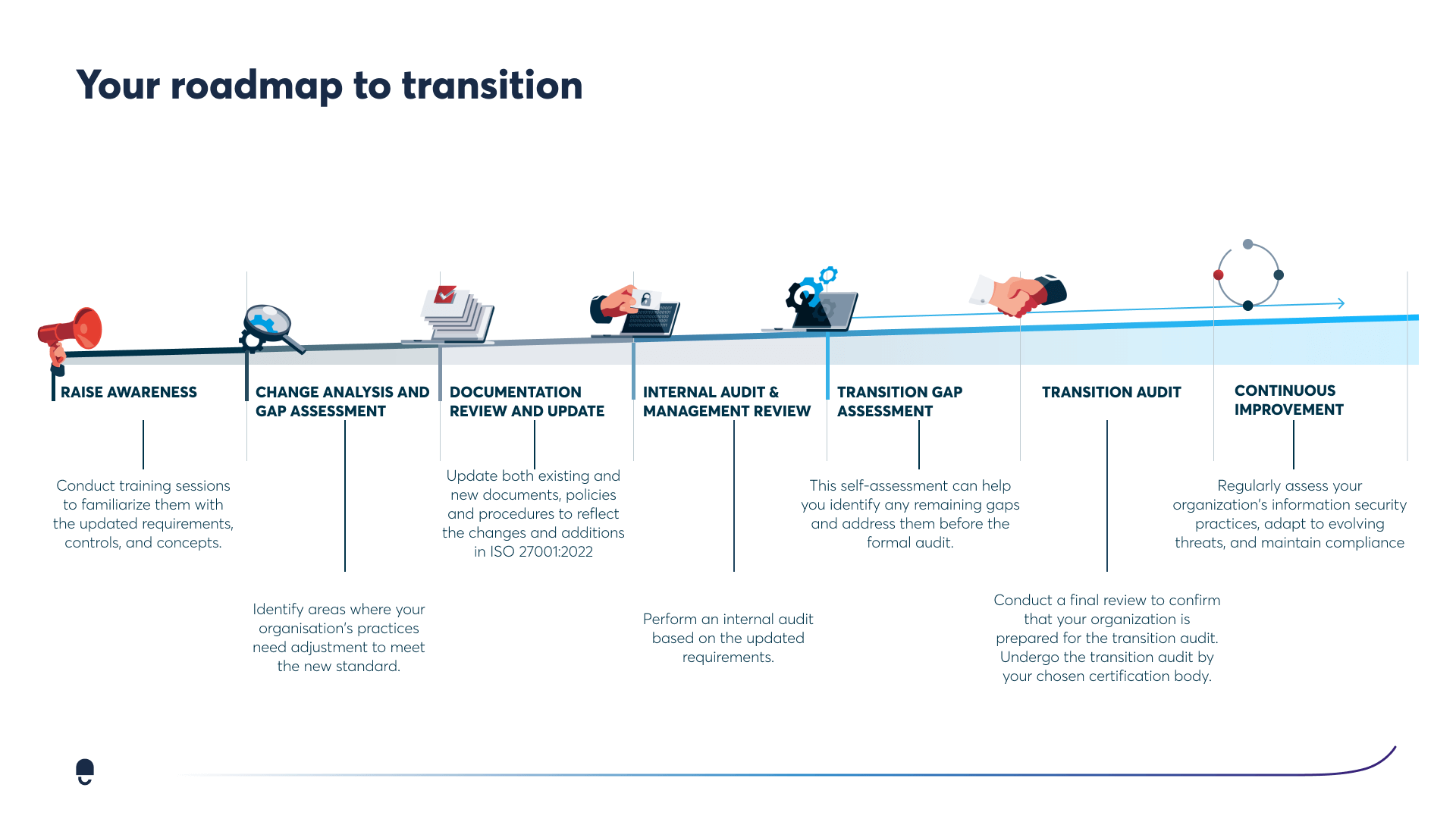
Here are the key steps in your roadmap to transition:
Raise awareness: The first step is to raise awareness of the transition within your organisation. This includes communicating the benefits of the new standard, as well as the timeline and requirements for the transition.
Conduct a change analysis and gap assessment: Once you have raised awareness, you need to conduct a change analysis and gap assessment. This will help you to identify the areas where your current information security management system (ISMS) needs to be updated to meet the requirements of ISO 27001:2022.
Review and update documentation: Once you have identified the gaps, you need to review and update your ISMS documentation. This includes your policies, procedures, and work instructions.
Perform an internal audit: Once your documentation is updated, you need to perform an internal audit to ensure that your ISMS is compliant with the new standard.
Conduct a transition gap assessment: After the internal audit, you need to conduct a transition gap assessment. This will help you to identify any remaining gaps that need to be addressed before you can transition to ISO 27001:2022.
Undergo a transition audit: Once you have addressed all of the gaps, you need to undergo a transition audit. This is a final check to ensure that your ISMS is compliant with the new standard.
Maintain continuous improvement: Once you have transitioned to ISO 27001:2022, it is important to maintain continuous improvement. This means regularly reviewing your ISMS to ensure that it is still effective in protecting your information assets.
In addition to these key steps, there are a few other things you can do to make the transition to ISO 27001:2022 smoother and more successful. These include (and are not limited to):
- Get buy-in from senior management.
- Involve all stakeholders in the transition process.
- Use a certified transition partner.
- Set realistic goals and milestones.
- Communicate regularly with stakeholders.
- By following these tips, you can make the transition to ISO 27001:2022 a success.
Here are some additional proactive business advice:
- Use the transition as an opportunity to improve your overall information security posture.
- Consider using the transition as a way to consolidate or streamline your ISMS processes.
- Use the transition to communicate the importance of information security to your employees and other stakeholders.
- Use the transition to improve your organisation's risk management capabilities.
By taking a proactive approach to the transition, you can make it a valuable asset to your organisation.
Expert Insights:
What is next for ISO 27001?
As is typical with ISO standards in general, they are all subject to updates over time, and ISO 27001:2022 will be no different.
As cybersecurity threats continue to grow — we can expect the standard to be reviewed more and more frequently. This is why we at DataGuard constantly advocate for staying on top of your ISMS.
On another note, with more focus on information security for the use of cloud services, we can expect top cloud providers such as AWS, GCP and Microsoft Azure to start cloud-offering out-of-the-box compliance solutions to support with the new ISO 27001:2022 through things like cloud configuration checks and data leakage prevention solutions.
Kyle Tackley
Team Lead – UK Tech and Privacy Practice
up to 50%
Cheaper than external consultants
up to 300%
Increase your opt-in rate with Consent & Preference Management
3 months
Get audit-ready in as little as three months
100%
First-try pass rate in external audits on ISO 27001 and TISAX®
Saves up to 100 hours
of manual work to get ISO 27001 certified or TISAX® labels
Customers trust us
P I C
PRIVACY
External DPO
Audit and risk analysis
Data Subject Requests
Online training courses
Cookie & Preference manager
Business advice from experts
INFOSEC
Prepare for ISO 27001
Build an ISMS
Cyber security
Asset management
Risk mitigation
Internal audit
COMPLIANCE
Digital whistleblowing system
Whistleblowing support
Compliance audit
Risk mitigation
Online training courses
Templates
ISO 27001:2022 requirements
|
4.1 Understanding the organisation and its context 4.2 Understanding the needs and expectations of interested parties 4.3 Determining the scope of the ISMS 4.4 Information security management system (ISMS) 5.2 Information Security Policy 5.3 Organisational roles, responsibilities and authorities 6.1 Actions to address risks and opportunities 6.2 Information security objectives and planning to achieve them 7.1 Resources 7.2 Competence |
7.3 Awareness 7.4 Communication 7.5 Documented information 8.1 Operational planning and control 8.2 Information security risk assessment 8.3 Information security risk treatment 9.1 Monitoring, measurement, analysis and evaluation 9.2 Internal audit 9.3 Management review 10.1 Nonconformity and corrective action 10.2 Continual improvement |
Trusted and used by companies








